Trauma Stabilization & Splinting
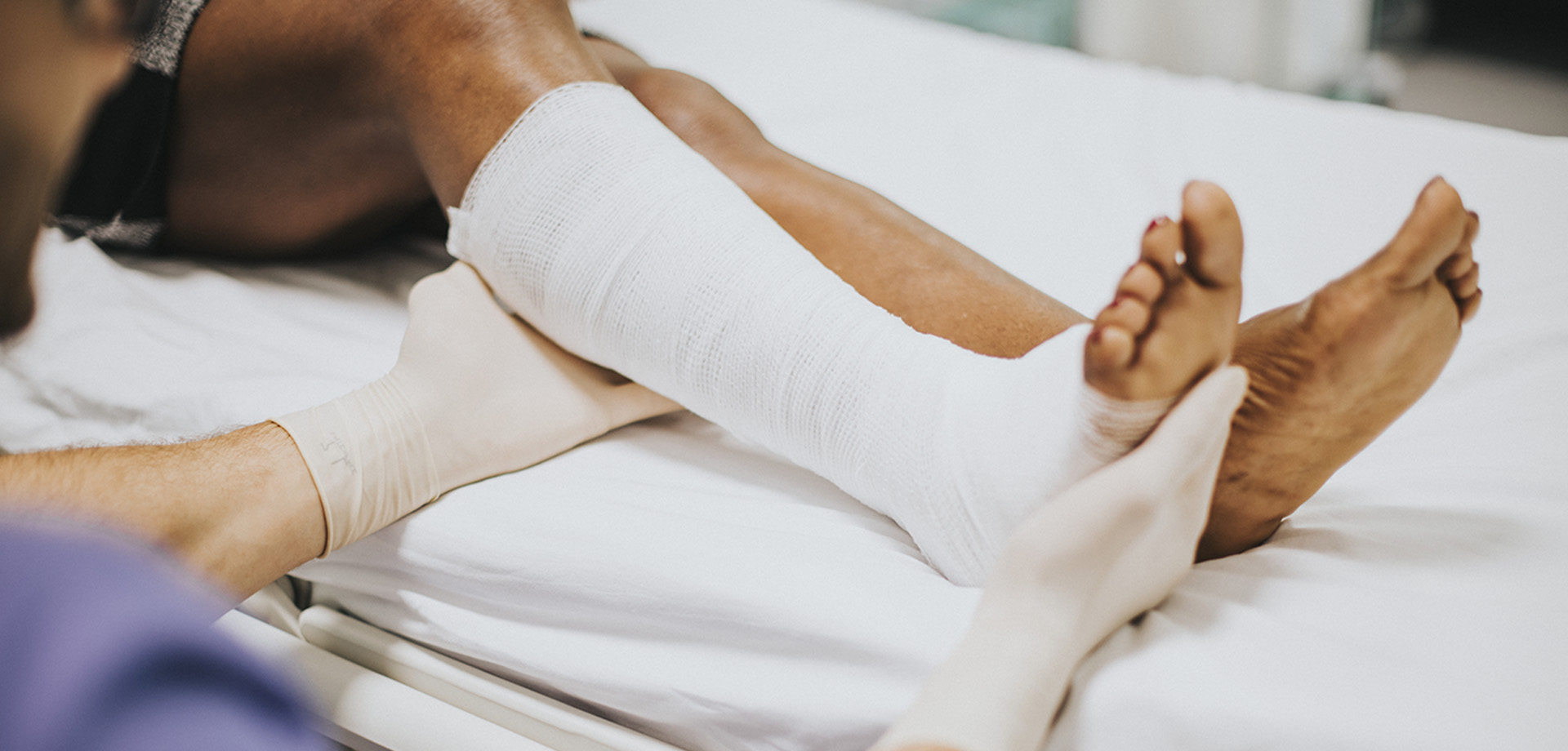
Trauma stabilization and splinting are critical components of emergency care, particularly in regions with high rates of road traffic accidents, workplace injuries, and falls. In the UAE, trauma cases form a significant portion of emergency department visits, requiring rapid assessment, structured stabilization, and immediate intervention to prevent complications and long-term disability.
The primary objective of trauma stabilization is to assess and manage life-threatening injuries using systematic protocols such as the Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) approach. The primary survey focuses on airway protection, breathing support, circulation stabilization, neurological status, and exposure assessment. Once vital functions are secured, attention shifts to secondary injuries such as fractures, dislocations, soft tissue damage, and internal bleeding.
Fractures are among the most common traumatic injuries. Immediate immobilization using splints prevents further bone displacement, reduces pain, and minimizes vascular or nerve damage. Splinting stabilizes the injured limb until definitive orthopedic treatment can be provided. Emergency physicians carefully assess circulation, sensation, and movement before and after splint application.
In cases of suspected spinal injury, strict spinal immobilization is maintained using cervical collars and spinal boards to prevent catastrophic neurological complications. Patients with head trauma are closely monitored for signs of intracranial bleeding or neurological deterioration.
Hemorrhage control is another essential aspect of trauma stabilization. Direct pressure, pressure dressings, tourniquets, and intravenous fluid resuscitation may be required to prevent shock. Rapid coordination with surgical teams ensures timely operative management when necessary.
Emergency departments in Dubai are equipped with trauma bays, portable imaging systems, ultrasound devices for internal bleeding detection, and rapid blood transfusion protocols. Multidisciplinary trauma teams, including emergency physicians, surgeons, anesthesiologists, and radiologists, collaborate for comprehensive care.
Pain management is integrated into trauma stabilization, ensuring patient comfort while avoiding masking critical symptoms. Advanced imaging such as X-rays and CT scans are coordinated promptly to confirm fracture patterns and internal injuries.
Beyond immediate stabilization, patient education and follow-up planning are essential to prevent long-term complications such as malunion, joint stiffness, or chronic pain. Rehabilitation pathways may be initiated early for optimal recovery.
Trauma stabilization and splinting serve as foundational emergency services that preserve life, protect limb function, and reduce long-term disability. Through structured assessment, rapid immobilization, and coordinated multidisciplinary care, emergency departments provide high-quality trauma management that improves patient outcomes across all age groups.
The primary objective of trauma stabilization is to assess and manage life-threatening injuries using systematic protocols such as the Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) approach. The primary survey focuses on airway protection, breathing support, circulation stabilization, neurological status, and exposure assessment. Once vital functions are secured, attention shifts to secondary injuries such as fractures, dislocations, soft tissue damage, and internal bleeding.
Fractures are among the most common traumatic injuries. Immediate immobilization using splints prevents further bone displacement, reduces pain, and minimizes vascular or nerve damage. Splinting stabilizes the injured limb until definitive orthopedic treatment can be provided. Emergency physicians carefully assess circulation, sensation, and movement before and after splint application.
In cases of suspected spinal injury, strict spinal immobilization is maintained using cervical collars and spinal boards to prevent catastrophic neurological complications. Patients with head trauma are closely monitored for signs of intracranial bleeding or neurological deterioration.
Hemorrhage control is another essential aspect of trauma stabilization. Direct pressure, pressure dressings, tourniquets, and intravenous fluid resuscitation may be required to prevent shock. Rapid coordination with surgical teams ensures timely operative management when necessary.
Emergency departments in Dubai are equipped with trauma bays, portable imaging systems, ultrasound devices for internal bleeding detection, and rapid blood transfusion protocols. Multidisciplinary trauma teams, including emergency physicians, surgeons, anesthesiologists, and radiologists, collaborate for comprehensive care.
Pain management is integrated into trauma stabilization, ensuring patient comfort while avoiding masking critical symptoms. Advanced imaging such as X-rays and CT scans are coordinated promptly to confirm fracture patterns and internal injuries.
Beyond immediate stabilization, patient education and follow-up planning are essential to prevent long-term complications such as malunion, joint stiffness, or chronic pain. Rehabilitation pathways may be initiated early for optimal recovery.
Trauma stabilization and splinting serve as foundational emergency services that preserve life, protect limb function, and reduce long-term disability. Through structured assessment, rapid immobilization, and coordinated multidisciplinary care, emergency departments provide high-quality trauma management that improves patient outcomes across all age groups.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7



 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000







