Thyroid Hormone Replacement
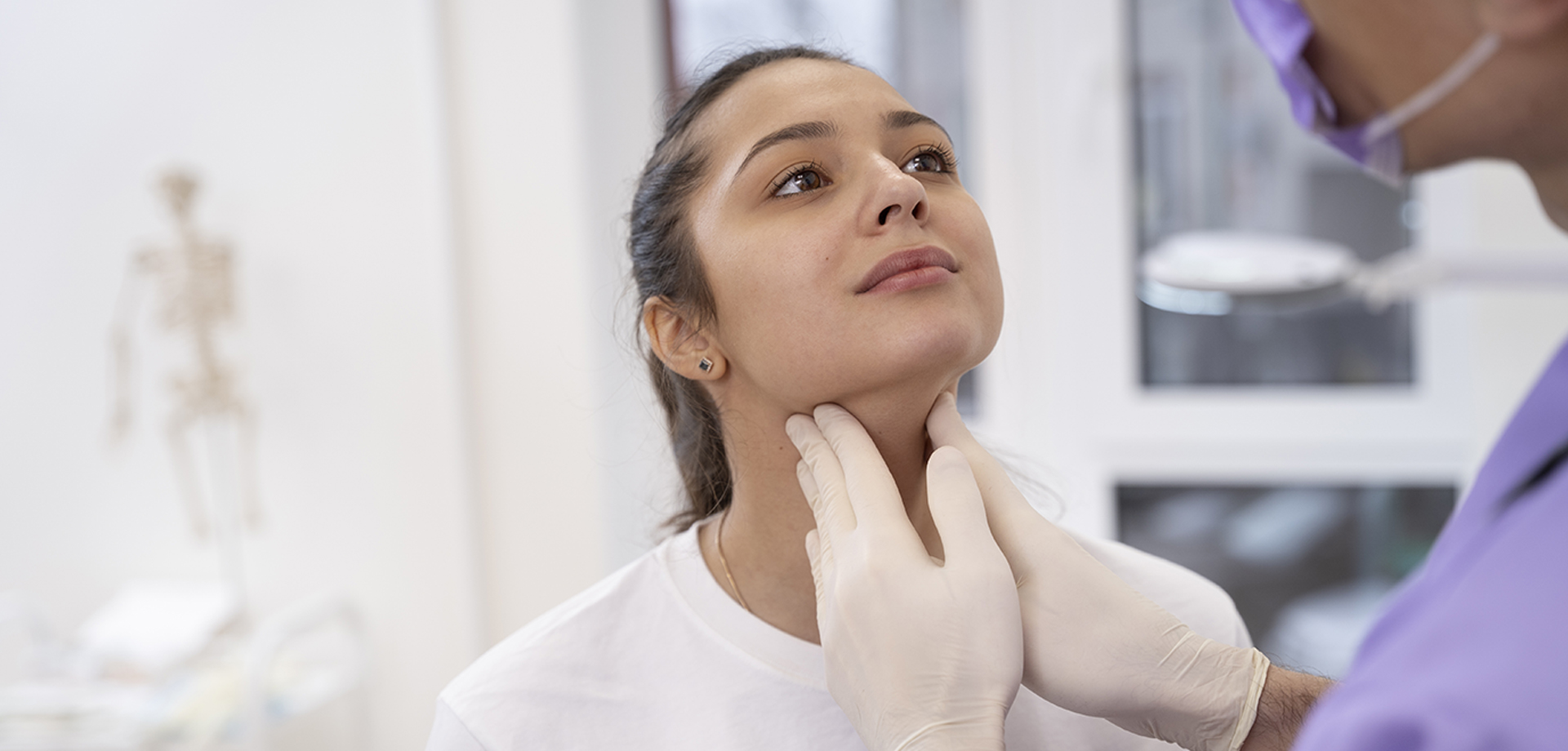
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for individuals with hypothyroidism and other conditions associated with insufficient thyroid hormone production. Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, cardiovascular function, thermoregulation, neurological activity, and growth. Deficiency leads to widespread systemic effects, making timely and accurate hormone replacement essential for restoring physiological balance.
Thyroid hormone replacement is most commonly indicated in primary hypothyroidism due to autoimmune thyroid disease, post-thyroidectomy states, radioactive iodine therapy, and congenital or iatrogenic thyroid hormone deficiency. The goal of therapy is to normalize thyroid hormone levels and relieve symptoms while maintaining stable metabolic function over the long term.
Treatment involves administration of synthetic thyroid hormone that closely mimics endogenous hormone activity. Dosing is individualized based on age, body weight, cardiac status, pregnancy, and severity of hormone deficiency. Initiation often begins at a calculated dose, followed by gradual adjustment guided by thyroid function testing and clinical response.
Monitoring is a critical component of thyroid hormone replacement. Blood tests are performed at regular intervals to ensure appropriate hormone levels and avoid under- or overtreatment. Overtreatment can lead to cardiovascular strain and bone loss, while undertreatment results in persistent symptoms and metabolic impairment.
Patient education is essential to treatment success. Patients are counseled on correct dosing, timing relative to meals and medications, and the importance of adherence. Special considerations are required during pregnancy, illness, or medication changes.
When managed appropriately, thyroid hormone replacement restores metabolic balance, improves quality of life, and prevents long-term complications. A structured endocrine approach ensures safe, effective, and lifelong management of thyroid hormone deficiency.
Thyroid hormone replacement is most commonly indicated in primary hypothyroidism due to autoimmune thyroid disease, post-thyroidectomy states, radioactive iodine therapy, and congenital or iatrogenic thyroid hormone deficiency. The goal of therapy is to normalize thyroid hormone levels and relieve symptoms while maintaining stable metabolic function over the long term.
Treatment involves administration of synthetic thyroid hormone that closely mimics endogenous hormone activity. Dosing is individualized based on age, body weight, cardiac status, pregnancy, and severity of hormone deficiency. Initiation often begins at a calculated dose, followed by gradual adjustment guided by thyroid function testing and clinical response.
Monitoring is a critical component of thyroid hormone replacement. Blood tests are performed at regular intervals to ensure appropriate hormone levels and avoid under- or overtreatment. Overtreatment can lead to cardiovascular strain and bone loss, while undertreatment results in persistent symptoms and metabolic impairment.
Patient education is essential to treatment success. Patients are counseled on correct dosing, timing relative to meals and medications, and the importance of adherence. Special considerations are required during pregnancy, illness, or medication changes.
When managed appropriately, thyroid hormone replacement restores metabolic balance, improves quality of life, and prevents long-term complications. A structured endocrine approach ensures safe, effective, and lifelong management of thyroid hormone deficiency.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7



 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000







