Oral Diabetes Medications Optimization
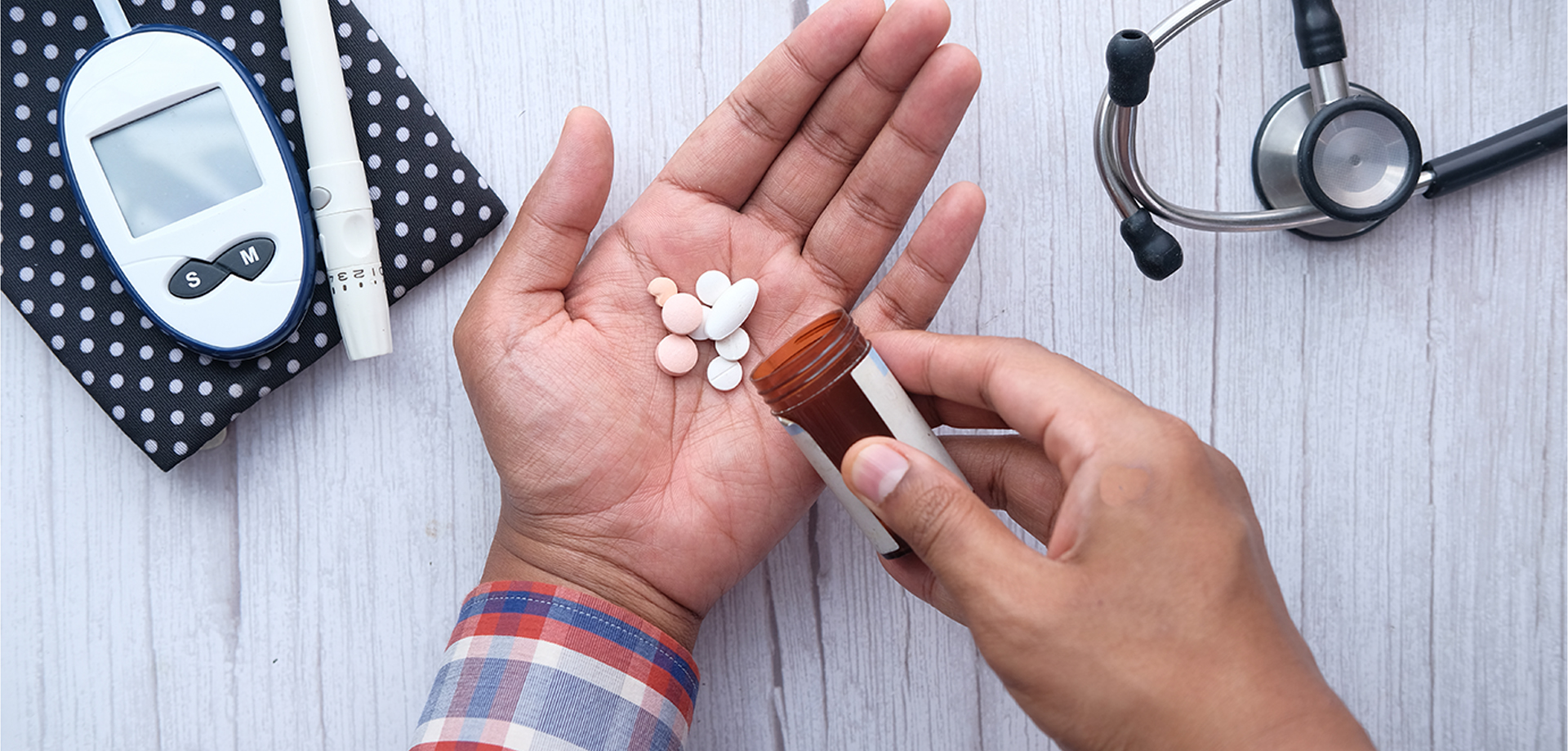

Oral diabetes medications optimization is a core component of effective Type 2 diabetes management and focuses on selecting, combining, and adjusting non-insulin therapies to achieve sustained glycemic control while minimizing side effects and long-term complications. With the expanding range of oral antidiabetic agents available today, optimization is no longer about prescribing a single drug but about developing a personalized, dynamic treatment strategy tailored to each patient’s metabolic profile and disease progression.
Type 2 diabetes is a heterogeneous condition driven by multiple pathophysiological mechanisms, including insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion, increased hepatic glucose production, and altered glucose absorption. Oral diabetes medications target these mechanisms through different pathways. Optimization begins with a comprehensive clinical assessment that includes current glycemic control, HbA1c trends, fasting and postprandial glucose levels, body weight, kidney and liver function, cardiovascular risk, and treatment adherence.
Initial therapy often starts with a foundational agent, but as diabetes progresses, combination therapy is frequently required. Optimization involves selecting complementary drug classes that work synergistically rather than duplicating mechanisms of action. This approach improves efficacy while reducing the risk of overtreatment, hypoglycemia, and unnecessary polypharmacy.
Regular medication review is a critical aspect of optimization. Many patients remain on suboptimal regimens for prolonged periods, leading to avoidable hyperglycemia and increased complication risk. Timely adjustment—whether escalation, substitution, or simplification—helps maintain glycemic targets and supports long-term metabolic stability. Optimization also considers the impact of medications on weight, blood pressure, lipid profile, and cardiovascular outcomes, moving beyond glucose control alone.
Safety is central to oral medication optimization. Renal function changes, aging, intercurrent illness, and drug interactions may necessitate dose modification or discontinuation of certain agents. Careful monitoring reduces adverse effects such as hypoglycemia, gastrointestinal intolerance, or fluid imbalance. In patients with established cardiovascular or kidney disease, medication choices are aligned with broader risk reduction goals.
Patient education and engagement are essential for successful optimization. Understanding dosing schedules, meal timing, potential side effects, and the importance of adherence improves treatment effectiveness. Addressing barriers such as medication fatigue, fear of escalation, or misconceptions about disease progression enhances long-term outcomes.
Oral diabetes medications optimization is not a one-time intervention but an ongoing process that evolves with the patient’s clinical status and life circumstances. When implemented within a structured endocrine care framework, optimized oral therapy delays the need for insulin, reduces complication risk, and supports sustainable diabetes control. A proactive, individualized approach ensures that oral medications remain effective tools throughout the continuum of diabetes care.
Type 2 diabetes is a heterogeneous condition driven by multiple pathophysiological mechanisms, including insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion, increased hepatic glucose production, and altered glucose absorption. Oral diabetes medications target these mechanisms through different pathways. Optimization begins with a comprehensive clinical assessment that includes current glycemic control, HbA1c trends, fasting and postprandial glucose levels, body weight, kidney and liver function, cardiovascular risk, and treatment adherence.
Initial therapy often starts with a foundational agent, but as diabetes progresses, combination therapy is frequently required. Optimization involves selecting complementary drug classes that work synergistically rather than duplicating mechanisms of action. This approach improves efficacy while reducing the risk of overtreatment, hypoglycemia, and unnecessary polypharmacy.
Regular medication review is a critical aspect of optimization. Many patients remain on suboptimal regimens for prolonged periods, leading to avoidable hyperglycemia and increased complication risk. Timely adjustment—whether escalation, substitution, or simplification—helps maintain glycemic targets and supports long-term metabolic stability. Optimization also considers the impact of medications on weight, blood pressure, lipid profile, and cardiovascular outcomes, moving beyond glucose control alone.
Safety is central to oral medication optimization. Renal function changes, aging, intercurrent illness, and drug interactions may necessitate dose modification or discontinuation of certain agents. Careful monitoring reduces adverse effects such as hypoglycemia, gastrointestinal intolerance, or fluid imbalance. In patients with established cardiovascular or kidney disease, medication choices are aligned with broader risk reduction goals.
Patient education and engagement are essential for successful optimization. Understanding dosing schedules, meal timing, potential side effects, and the importance of adherence improves treatment effectiveness. Addressing barriers such as medication fatigue, fear of escalation, or misconceptions about disease progression enhances long-term outcomes.
Oral diabetes medications optimization is not a one-time intervention but an ongoing process that evolves with the patient’s clinical status and life circumstances. When implemented within a structured endocrine care framework, optimized oral therapy delays the need for insulin, reduces complication risk, and supports sustainable diabetes control. A proactive, individualized approach ensures that oral medications remain effective tools throughout the continuum of diabetes care.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7



 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000







