Insulin Initiation & Titration
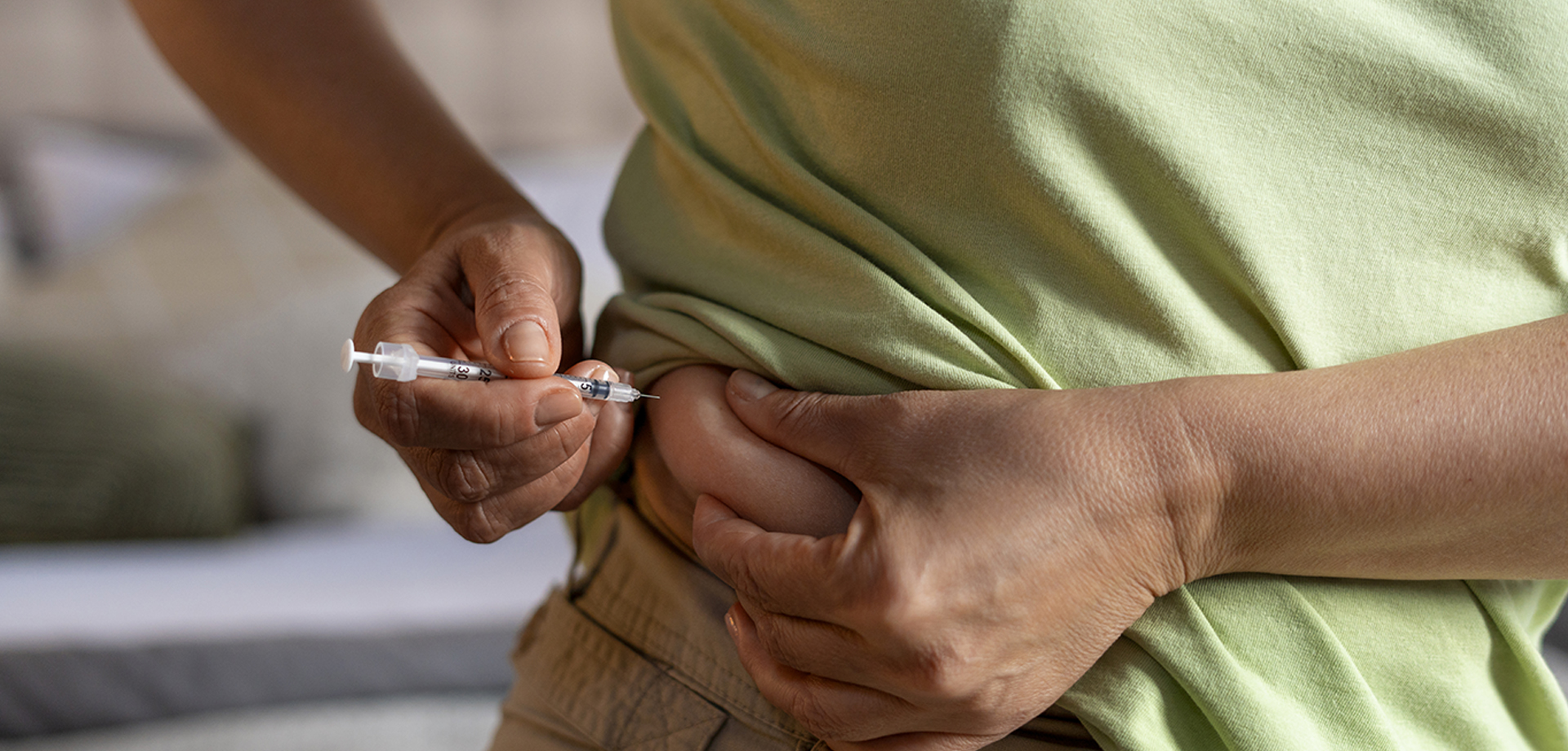
Insulin initiation and titration are essential components of effective diabetes management for individuals who are unable to achieve or maintain optimal glycemic control through lifestyle modification and non-insulin therapies alone. Insulin is a life-sustaining therapy for people with Type 1 diabetes and an important treatment option for many individuals with Type 2 diabetes, particularly as the disease progresses or during periods of metabolic stress.
Insulin initiation refers to the structured introduction of insulin therapy, while titration involves the ongoing adjustment of insulin doses based on glucose patterns, clinical response, and individual patient needs. The primary goal is to mimic physiological insulin secretion as closely as possible while minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia and excessive weight gain. Successful insulin management requires a personalized, methodical approach rather than a one-size-fits-all strategy.
In Type 2 diabetes, insulin is commonly initiated when oral or injectable non-insulin medications fail to maintain target blood glucose levels, when HbA1c remains persistently elevated, or during situations such as acute illness, surgery, pregnancy, or severe hyperglycemia. Basal insulin is often the first step, providing steady background insulin to control fasting glucose levels. In Type 1 diabetes, insulin must be initiated immediately at diagnosis using a comprehensive basal–bolus regimen to replace absent endogenous insulin.
Titration is a continuous and dynamic process that relies on regular blood glucose monitoring and trend analysis rather than isolated readings. Fasting, pre-meal, and post-meal glucose values guide dose adjustments, allowing insulin therapy to be fine-tuned over time. Structured titration protocols improve safety and empower patients to participate in dose adjustment under medical guidance, leading to better adherence and outcomes.
Patient education is a cornerstone of insulin initiation and titration. Individuals are trained in injection techniques, insulin storage, dose timing, glucose monitoring, and recognition and management of hypoglycemia. Addressing emotional and psychological barriers, such as fear of injections or concerns about dependency, is essential for long-term success. Education also includes sick-day rules, travel guidance, and lifestyle considerations to ensure safe insulin use in real-world settings.
Insulin requirements are not static. Changes in diet, physical activity, body weight, stress levels, intercurrent illness, or concurrent medications may necessitate dose adjustments. Regular follow-up and data review allow timely optimization and prevent prolonged periods of poor control or recurrent hypoglycemia.
When initiated and titrated correctly, insulin therapy significantly improves glycemic control, reduces the risk of acute and chronic diabetes complications, and enhances quality of life. A structured insulin initiation and titration program, delivered through multidisciplinary endocrine care, ensures that insulin is used safely, effectively, and confidently as part of comprehensive diabetes management.
Insulin initiation refers to the structured introduction of insulin therapy, while titration involves the ongoing adjustment of insulin doses based on glucose patterns, clinical response, and individual patient needs. The primary goal is to mimic physiological insulin secretion as closely as possible while minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia and excessive weight gain. Successful insulin management requires a personalized, methodical approach rather than a one-size-fits-all strategy.
In Type 2 diabetes, insulin is commonly initiated when oral or injectable non-insulin medications fail to maintain target blood glucose levels, when HbA1c remains persistently elevated, or during situations such as acute illness, surgery, pregnancy, or severe hyperglycemia. Basal insulin is often the first step, providing steady background insulin to control fasting glucose levels. In Type 1 diabetes, insulin must be initiated immediately at diagnosis using a comprehensive basal–bolus regimen to replace absent endogenous insulin.
Titration is a continuous and dynamic process that relies on regular blood glucose monitoring and trend analysis rather than isolated readings. Fasting, pre-meal, and post-meal glucose values guide dose adjustments, allowing insulin therapy to be fine-tuned over time. Structured titration protocols improve safety and empower patients to participate in dose adjustment under medical guidance, leading to better adherence and outcomes.
Patient education is a cornerstone of insulin initiation and titration. Individuals are trained in injection techniques, insulin storage, dose timing, glucose monitoring, and recognition and management of hypoglycemia. Addressing emotional and psychological barriers, such as fear of injections or concerns about dependency, is essential for long-term success. Education also includes sick-day rules, travel guidance, and lifestyle considerations to ensure safe insulin use in real-world settings.
Insulin requirements are not static. Changes in diet, physical activity, body weight, stress levels, intercurrent illness, or concurrent medications may necessitate dose adjustments. Regular follow-up and data review allow timely optimization and prevent prolonged periods of poor control or recurrent hypoglycemia.
When initiated and titrated correctly, insulin therapy significantly improves glycemic control, reduces the risk of acute and chronic diabetes complications, and enhances quality of life. A structured insulin initiation and titration program, delivered through multidisciplinary endocrine care, ensures that insulin is used safely, effectively, and confidently as part of comprehensive diabetes management.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7



 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000







