Cauterization for Epistaxis
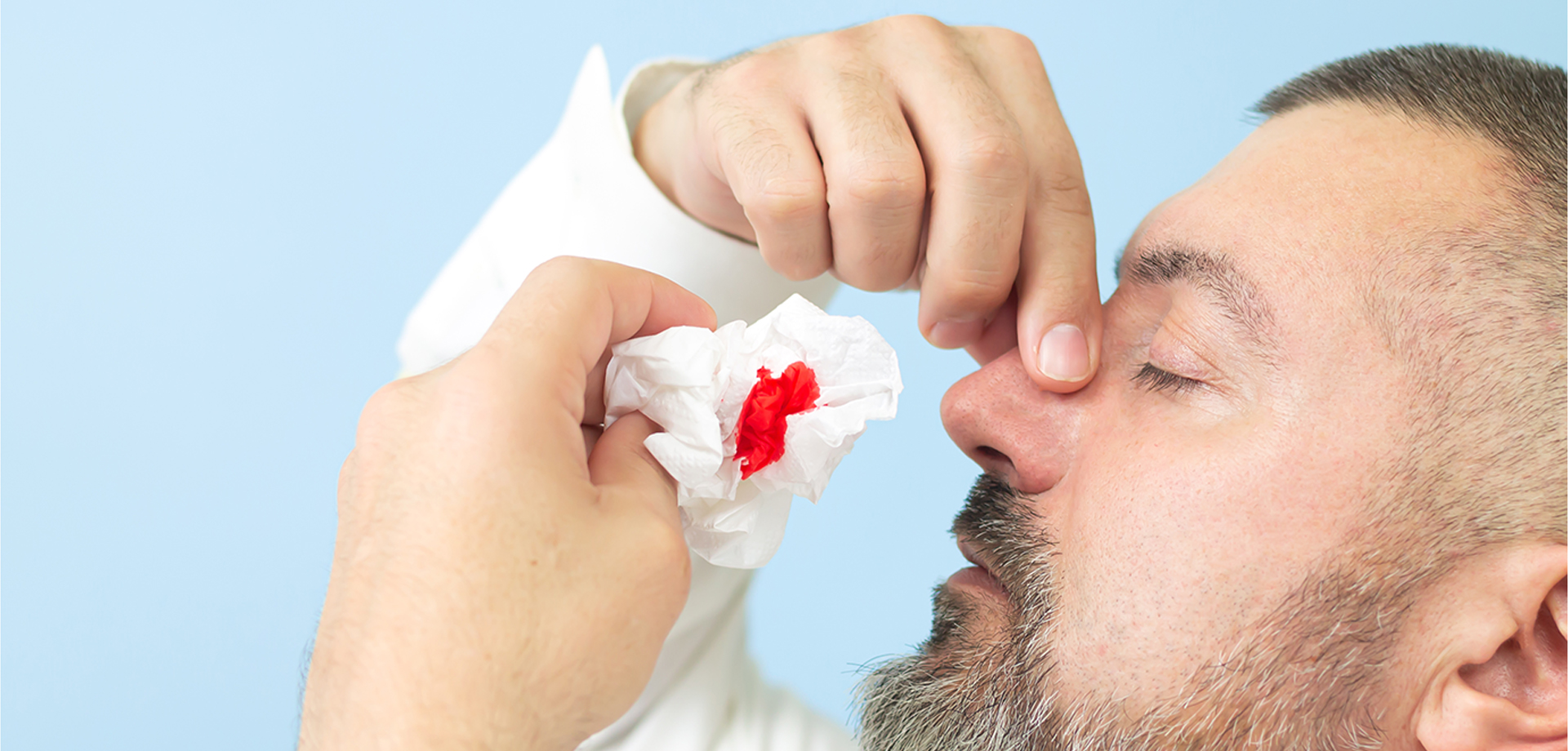

Cauterization for epistaxis is a targeted ENT procedure used to control recurrent nosebleeds by sealing fragile or bleeding blood vessels within the nasal lining. Epistaxis is a common condition affecting individuals of all ages, often resulting from dry air, trauma, nasal inflammation, hypertension, or fragile superficial vessels in the anterior nasal septum. While most nosebleeds are self-limited, recurrent or persistent episodes require structured evaluation and intervention.
The majority of nosebleeds originate from a region in the front part of the nasal septum where small blood vessels are densely concentrated. In some individuals, these vessels become fragile due to dryness, irritation, allergies, or underlying vascular conditions. Repeated bleeding episodes can be distressing and interfere with daily activities.
Evaluation begins with a detailed history and nasal examination using appropriate visualization tools. Identification of the bleeding point is crucial for effective treatment. In cases of frequent unilateral nosebleeds, cauterization provides a localized solution by sealing the offending vessel.
The procedure involves application of a cauterizing agent or controlled energy to the bleeding site. It is performed in an outpatient setting under local anesthesia. The process is brief and generally well tolerated. After treatment, patients may experience mild discomfort or crusting but can usually resume normal activities shortly thereafter.
Post-procedure care includes nasal hydration, avoidance of nose picking or forceful blowing, and environmental moisture control. Follow-up ensures proper healing and evaluates recurrence risk.
Cauterization is a safe and effective treatment for recurrent anterior epistaxis. By targeting the specific bleeding vessel, it reduces recurrence frequency and provides long-term control while minimizing the need for more invasive interventions.
The majority of nosebleeds originate from a region in the front part of the nasal septum where small blood vessels are densely concentrated. In some individuals, these vessels become fragile due to dryness, irritation, allergies, or underlying vascular conditions. Repeated bleeding episodes can be distressing and interfere with daily activities.
Evaluation begins with a detailed history and nasal examination using appropriate visualization tools. Identification of the bleeding point is crucial for effective treatment. In cases of frequent unilateral nosebleeds, cauterization provides a localized solution by sealing the offending vessel.
The procedure involves application of a cauterizing agent or controlled energy to the bleeding site. It is performed in an outpatient setting under local anesthesia. The process is brief and generally well tolerated. After treatment, patients may experience mild discomfort or crusting but can usually resume normal activities shortly thereafter.
Post-procedure care includes nasal hydration, avoidance of nose picking or forceful blowing, and environmental moisture control. Follow-up ensures proper healing and evaluates recurrence risk.
Cauterization is a safe and effective treatment for recurrent anterior epistaxis. By targeting the specific bleeding vessel, it reduces recurrence frequency and provides long-term control while minimizing the need for more invasive interventions.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7



 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000







