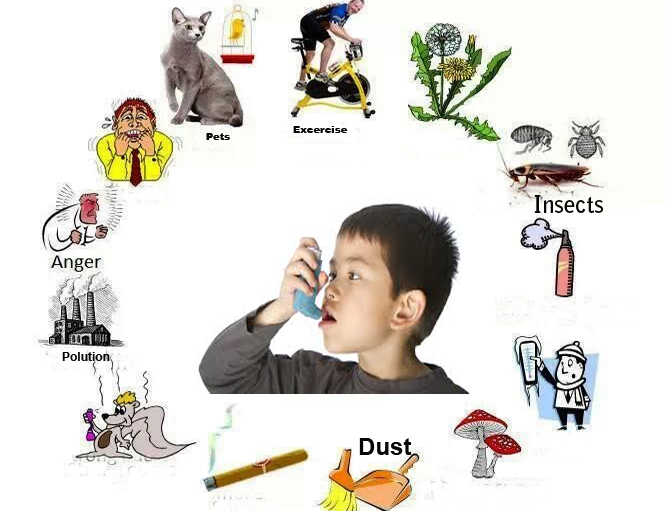
31st May of every year is observed as No Tobacco Day. In present world where everyone talks about COVID, let’s look in to some of the aspects related to smoking which is connected to COVID-19.
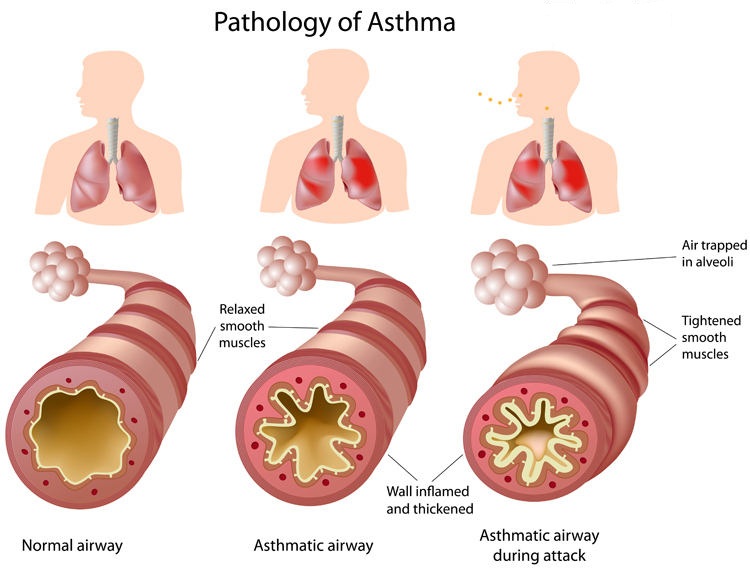
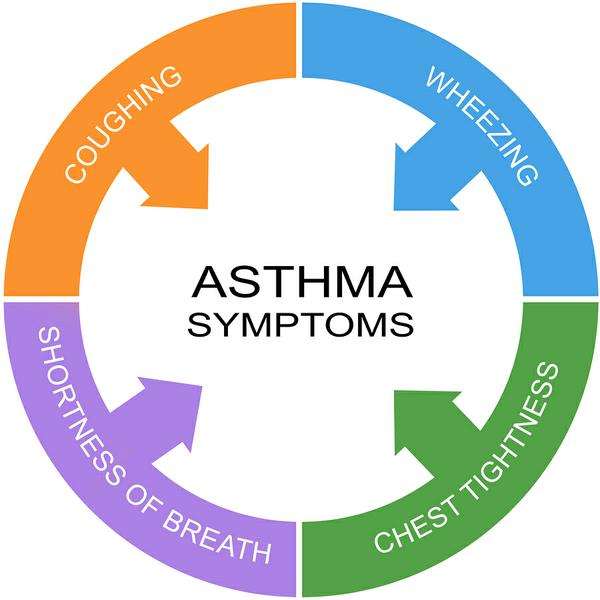
Smoking any kind of tobacco reduces lung capacity and increases the risk of many respiratory infections and can increase the severity of respiratory diseases. COVID-19 is an infectious disease that primarily attacks the lungs. Smoking impairs lung function making it harder for the body to fight off coronaviruses and other respiratory diseases. Available research suggests that smokers are at higher risk of developing severe COVID-19 outcomes.
Using smokeless tobacco often involves some hand to mouth contact. Another risk associated with using smokeless tobacco products, like chewing tobacco, is that the virus can be spread when the user spits out the excess saliva produced during the chewing process.

Precautions
• Do not share devices like waterpipes and e-cigarettes.
• Spread the word about the risks of smoking, using e-cigarettes and using smokeless tobacco.
• Protect others from the harms of second-hand smoke.
• Know the importance of washing your hands, physical distancing, and not sharing any smoking or e -cigarette products.
• Do not spit in public places
#TobaccoExposed
• Tobacco products kill more than 8 million people every year. Tobacco and related industries must continuously find new consumers to replace the ones that their products are killing to maintain revenue.
• Tobacco companies spent over USD 9 billion in marketing and advertising and the world lost 8 million lives from causes related to tobacco use and exposure to second-hand smoke.
• We want to create a generation that is free from tobacco and second-hand smoke and the death and disease that they cause.
• Break free from the tobacco and related industries’ manipulation by becoming educated on their tactics and the harm caused by their products.
• Tobacco use is responsible for 25% of all cancer deaths globally. Use of nicotine and tobacco products increases the risk of cancer, cardiovascular and pulmonary disease.
• Over 1 million people die from second-hand smoke exposure every year.
• Children and adolescents who use e-cigarettes at least double their chance of smoking cigarettes later in life.
• E-cigarette use increases your risk of heart disease and lung disorders.
• Nicotine in e-cigarettes is a highly addictive drug and can damage children’s developing brains.
• Smoking shisha is just as harmful as other forms of tobacco use.