What is a Cataract?
A cataract is a clouding of the eye’s lens, which blocks or changes the passage of light into the eye. The lens of the eye is located behind the pupil and the colored iris, and is normally transparent. The lens helps to focus images onto the retina – which transmits the images to the brain.
Am I at risk for developing cataracts?
The exact cause of a cataract is unknown. Most often, a cataract is part of getting older. As you age, you are at greater risk of developing a cataract. There are also several possible risk factors for cataracts, such as:
• Intense heat or long-term exposure to UV rays from the sun
• Certain diseases, such as diabetes
• Inflammation in the eye
• Hereditary influences
• Events before birth, such as German measles in the mother
• Long-term steroid use
• Eye injuries
• Eye diseases
• Smoking
What are the symptoms of a cataract?
Generally, a cataract does not cause pain, redness or tears. The following problems may indicate that you have a cataract:
• You have blurred vision, double vision, ghost images, or the sense of a “film” over your eyes.
• Lights seem too dim for reading or close-up work, or you are “dazzled” by strong light.
• You change eyeglass prescriptions often and the change does not seem to help your vision.
• You may also be able to see the cataract in your eye. It may look like a milky or yellowish spot in your pupil.
Why do cataracts form?
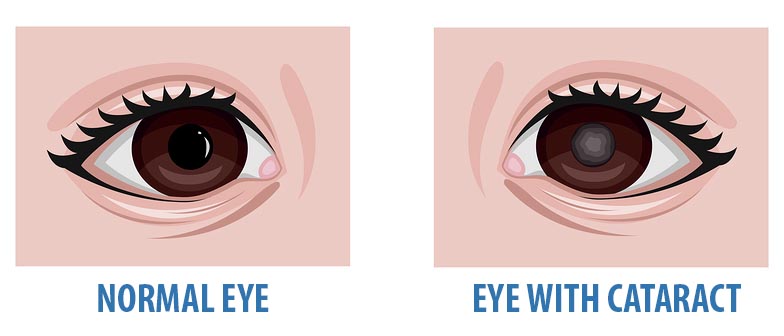
Cataracts are probably caused by changes related to aging. Throughout our lives, our bodies replace old cells with new ones. As we grow older, the old cells in our eye’s lens build up and block light as it tries to pass through. The end result is cloudy vision.
As mentioned earlier, besides getting older, other factors may cause cataracts to form. Each of these factors lead to a metabolic pathway which leads to cloudiness of the otherwise transparent lens..
How will my eye doctor (Ophthalmologist) check for cataracts?
Everyone who gets a cataract experiences it differently. But a person with a cataract commonly experiences cloudy or blurry vision. Lights may cause a glare, seem too dim or seem too bright. It may be hard to read or drive, especially at night. If you have a cataract, you may see halos around lights, such as car headlights, that make it hard to focus clearly. Colors may not seem as bright as they used to be. Or you may have to change your eyeglass prescription often.
If you notice any of these changes, make an appointment to see your eye doctor.
If you have a cataract, you may have symptoms that are similar to those of other eye diseases. Only your eye doctor can tell you for sure what’s wrong.
To find out if you have cataracts, your eye doctor will want to:
• Find out your general medical history
• Find out your specific eye history, including problems and symptoms
• Test your vision (visual acuity)
• Test your side vision (peripheral vision)
• Test your eye movement
• Test you for glaucoma (by measuring the eye’s internal pressure)
• Do a microscopic exam of the front of the eye (using something called a slit lamp) to assess the density of the cataract and how it interferes with light passing through the lens
• Widen (dilate) the pupils of your eyes to examine the retina, the optic nerve (which carries visual messages from the retina to the brain) and the macula (responsible for the best part of central vision)
• Test you to see how glare affects your vision
After this exam, your eye doctor will determine whether you have cataracts, how much they interfere with your vision, whether surgery would help, and what types of treatment and lens replacements are best for you.