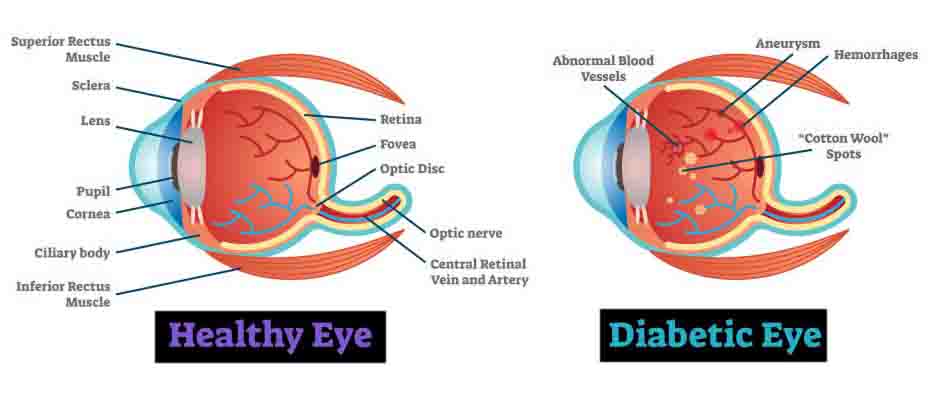
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetics are at risk of developing certain eye conditions. These include cataract, diabetic retinopathy and problems involving the optic nerve. A common manifestation of diabetes in the eye is diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy is basically a disorder of the retinal blood vessels. The retina is the light sensitive membrane in your eye that enables vision. Damage to the retinal blood vessels can cause vision loss or even blindness.
When the blood glucose levels fluctuate, the cells that line the blood vessels swell and become damaged. As a result, the blood vessels may leak fluid or blood into the retina and causes vision loss. As the blood vessels become increasingly damaged with poor blood sugar control, they can become completely obstructed, depleting the retina of blood and nutrients. Abnormal new blood vessels may then grow, and possibly bleed into the cavity of the eye, causing a more severe vision loss.
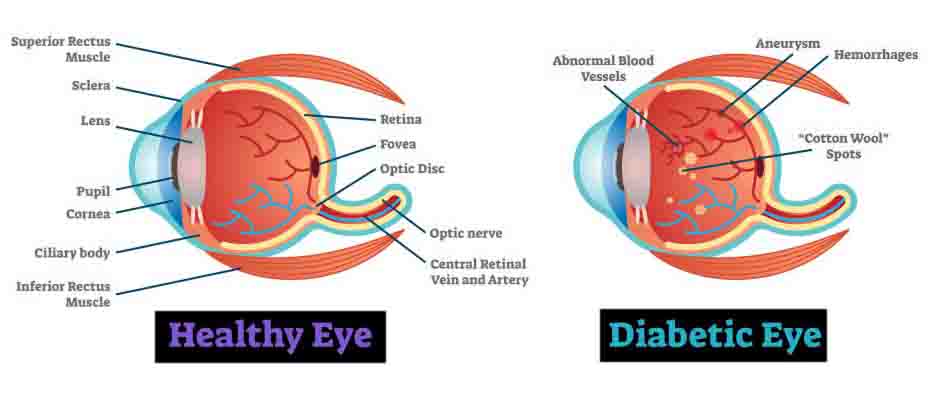
Who is at risk of developing Diabetic Retinopathy?
All people with diabetes are at risk of eye disease. In younger people with diabetes the onset can be rapid, whereas in older people it may come on more slowly. After ten-fifteen years of the disease most people with diabetes will have some degree of retinopathy. Incidence also increases with associated hypertension, other retinal diseases, smoking, sedentary lifestyle.
What are the symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy?
a) Blurred vision (often linked to blood sugar levels)
b) Floaters and flashes
c) Sudden loss of vision.
How is Diabetic Retinopathy treated?
There are two basic types of retinopathy:
a) Non Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy- It is the milder form, and patients may not have any symptoms initially. Retina shows tiny blood spots and fatty cholesterol deposits. Detection is through regular screening with Ophthalmologist. Diabetic patients who have vision problems from retinopathy can usually be successfully managed with laser and/or other treatment options. Early treatment is better for providing a successful outcome.
b) Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy- New blood vessels and fibrous tissue grow on the surface of the retina. When this tissue contracts it gives rise to bleeding inside the eye (vitreous hemorrhage) or it can pull the retina causing detachment. Both these lead to sudden loss of vision. Sometimes in such cases retinal surgery is required.
How to prevent Diabetic Retinopathy?
a) Good control of the blood sugars will reduce the risk of retinopathy
b) Control of hypertension
c) Avoid Smoking
d) Regular eye checks including a retinal examination by Ophthalmologist is by far the most important preventive measure for avoiding diabetic vision loss.
e) Close monitoring of your diabetes by your family doctor is also imperative.
f) Special care needs to be taken by diabetic patients who are pregnant.